UX Strategy

“If you gather data from users and then incorporate your findings into your product design, you’ll be more likely to meet their true needs. In return, they will probably like the end result better and become more efficient at using it.”
The UX journey for me always starts with data gathering activities. These various activities are crucial in the success of any project and should never be skipped.
Data gathering activities consist of:
- Site visits and interviews
- Personas
- Journey Maps
- Service Blueprints
Site Visits and User Interviews
Site Visits: Observing how a user interacts with an application provides information about people, their tasks, and their needs. Often, research participants don’t know why they do things, what they really need, or what they might do in the future. To really understand what people do, you can’t just ask them, you have to observe them. Most site visits can be either naturalistic or shadowing in nature, although I usually perform a hybrid of both.
User Interviews: Interviews give insight into what users think about a site, an application, a product or a process. User interviews form a complimentary research activity along with site visits. Interviews are a quick way to create a sense of how users feel, think, and what they perceive to be true. A typical interview session starts with generalized questions which lead to more specific ones, aimed at uncovering perspectives, pain points, goals and user needs.
These answers are then compiled for discovery of trends and common issues and then combined with the results from the site visits to assist with the next steps of the UX strategy; Personas, Journey Maps and Service Blueprints.
Personas
Personas are imaginary, yet realistic and descriptions of the users of your product. They provide the basis for design discussions by concentrating many pieces of user data into key focused, believable descriptions of your primary audience.
Personas usually start with Assumption Personas and then move on to Data Driven Personas as more information is uncovered.

Assumptive Personas
- Use the data you already have
- Make assumptions where needed
- Must be verified as more data is collected

Data-Driven Personas
- Every statement is backed up by data points
- Makes the personas much more believable and defensible
- Need various sources data that relate to your target audience
- Field Visits
- User Interviews
- Market Research
Personas Usage

Personas can streamline conversations and help with discussion around the priority of features. They help remove personal opinions and create empathy with the actual users of your design and technology. When applying them to conversations they replace “I think”, with “Our primary persona needs…”
Customer Journey Maps
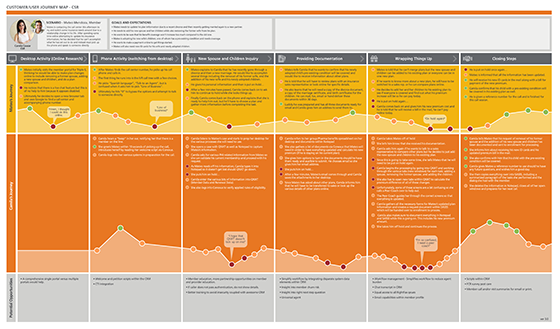
Customer Journey Maps are a visualization of the series of interactions a person has with a company while attempting to accomplish a goal over time and across channels. They are used for understanding and addressing customer needs and pain points.
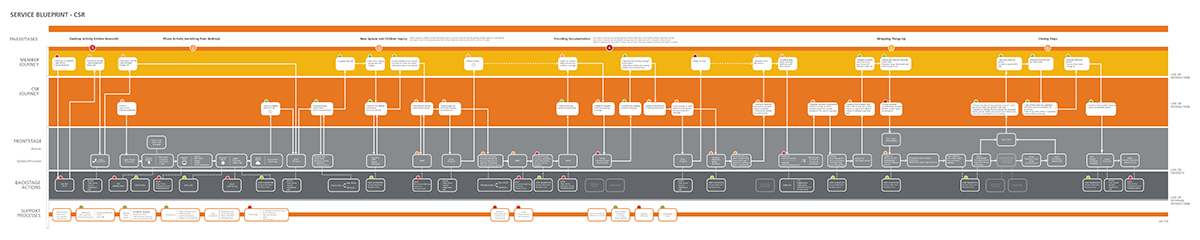
Service Blueprints
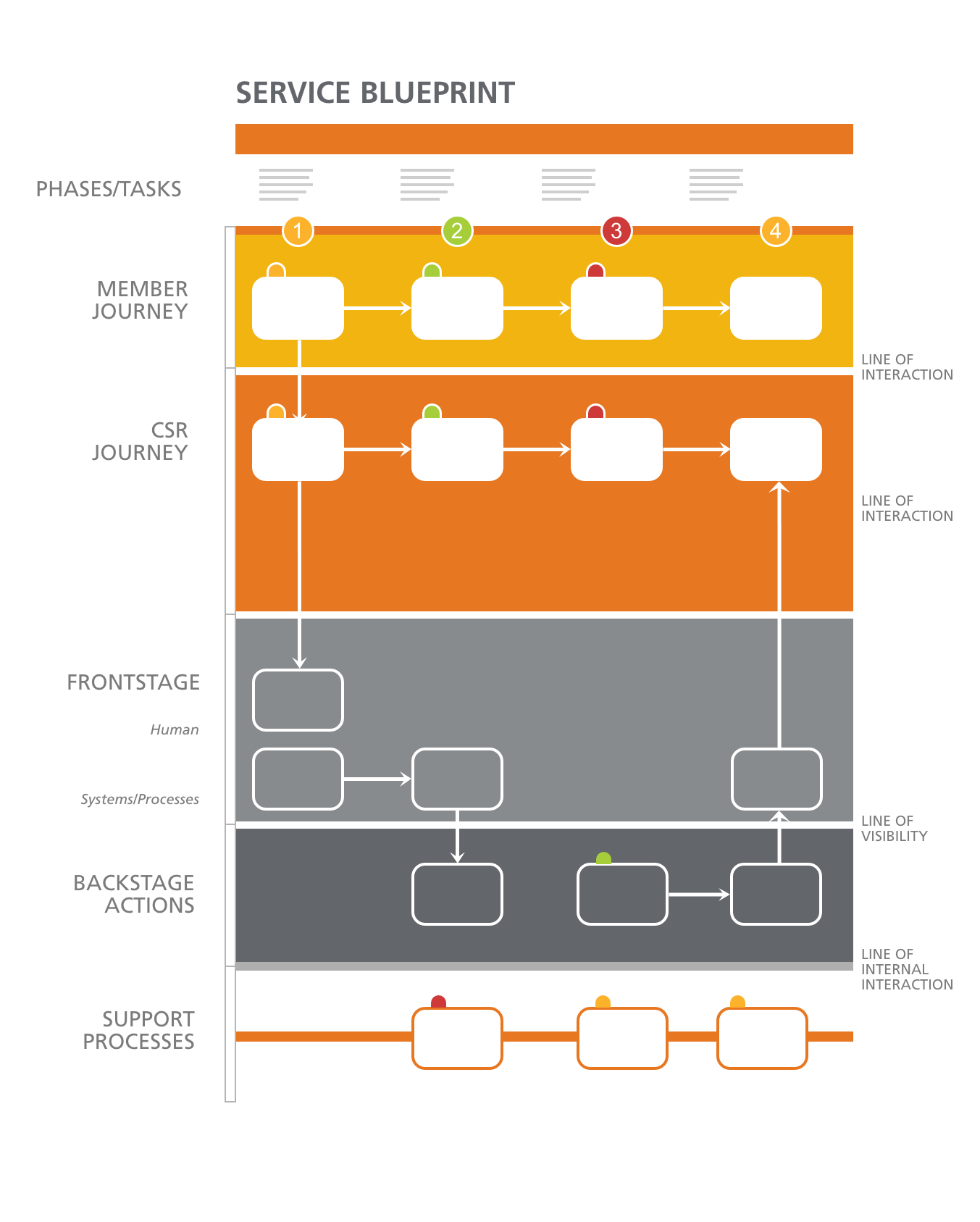
Service blueprints are tools used to visualize all the variables and relationships between different service components that are directly tied to touchpoints in a specific customer journey.


Recent Comments